Think of prompt engineering as the art and science of talking to an AI. It's how you craft instructions—or "prompts"—to guide a Large Language Model (LLM) to give you exactly what you want. This isn't about coding; it's about strategic communication. It’s the skill of asking the right question, in the right way, to get the best possible answer.
Demystifying Prompt Engineering And Why It Matters
Imagine you have a new team member who is brilliant, has encyclopedic knowledge, and can write, code, and solve problems at lightning speed. The catch? This assistant is extremely literal and has zero real-world experience or intuition. It will only do exactly what you tell it to, so you have to be crystal clear with your directions. That’s precisely what it’s like working with today's AI.
Prompt engineering is the crucial link between what you’re thinking and what the machine creates. It’s the practice of structuring your requests with the perfect mix of context, rules, and examples to steer the AI’s response in the right direction. If you give a vague prompt like, "Write about our new software," you'll likely get a bland, generic paragraph that isn't very useful. But a well-engineered prompt can produce a perfectly toned, detailed, and accurate feature announcement tailored to a specific audience.
The Shift From Programming To Instructing
For decades, getting a computer to do something meant writing code in a programming language. Prompt engineering flips that on its head. Instead of writing rigid code, you’re instructing a powerful, pre-trained model using plain English. This shift has made advanced AI accessible to everyone, from marketers brainstorming ad copy to support agents drafting empathetic replies to customers.
This skill really started gaining traction after the release of GPT-3 in May 2020. By 2023, it was a full-blown discipline. One survey showed that 75% of AI professionals considered input manipulation essential for getting good results from a model, confirming a direct link between prompt quality and output quality. Of course, things exploded after ChatGPT's release in 2022, when prompt engineering quickly became recognized as a vital business skill. You can learn more about its journey from niche concept to mainstream practice in this overview of prompt engineering's evolution.
Why This Skill Is A Game-Changer
Getting good at prompt engineering isn't just a nice-to-have technical skill; it's a real competitive advantage. For any business, especially in customer-facing roles, it has a direct impact on both efficiency and quality. An AI support agent, guided by precise prompts, can resolve customer issues faster, deliver more accurate information, and consistently stick to the company's brand voice.
A well-crafted prompt transforms an AI from a simple tool into a powerful, context-aware partner capable of executing complex tasks with precision.
Ultimately, learning what prompt engineering is and how to do it well delivers some major benefits:
- Greater Accuracy: You get outputs that are far more relevant and factually correct.
- Improved Efficiency: You spend less time correcting bad AI responses and more time getting work done.
- Enhanced Control: You can dictate the exact tone, style, format, and length of the AI's output.
- Increased Creativity: Prompts can be used to brainstorm and explore new ideas you might not have thought of otherwise.
It’s the key to unlocking the true power of generative AI, turning a fascinating piece of technology into a reliable and indispensable part of your toolkit.
The Core Principles of Crafting Great Prompts
Knowing what prompt engineering is gets you in the door, but mastering it means learning a few foundational rules. Think of it like a great chef who relies on core principles of flavor, balance, and texture—not just a recipe. A skilled prompt engineer uses a similar mental framework to build instructions that get the job done right the first time.
These principles are what turn a simple question into a powerful command.
At its core, a great prompt stands on four key pillars: clarity, context, constraints, and persona. Each one plays a vital role in shaping the AI's output, transforming it from a generic guess into a precise, targeted response. Once you internalize these concepts, you'll stop just asking questions and start strategically directing a powerful tool.
This diagram shows the basic flow: your input is carefully shaped into a prompt, which then guides the AI to produce a specific output.
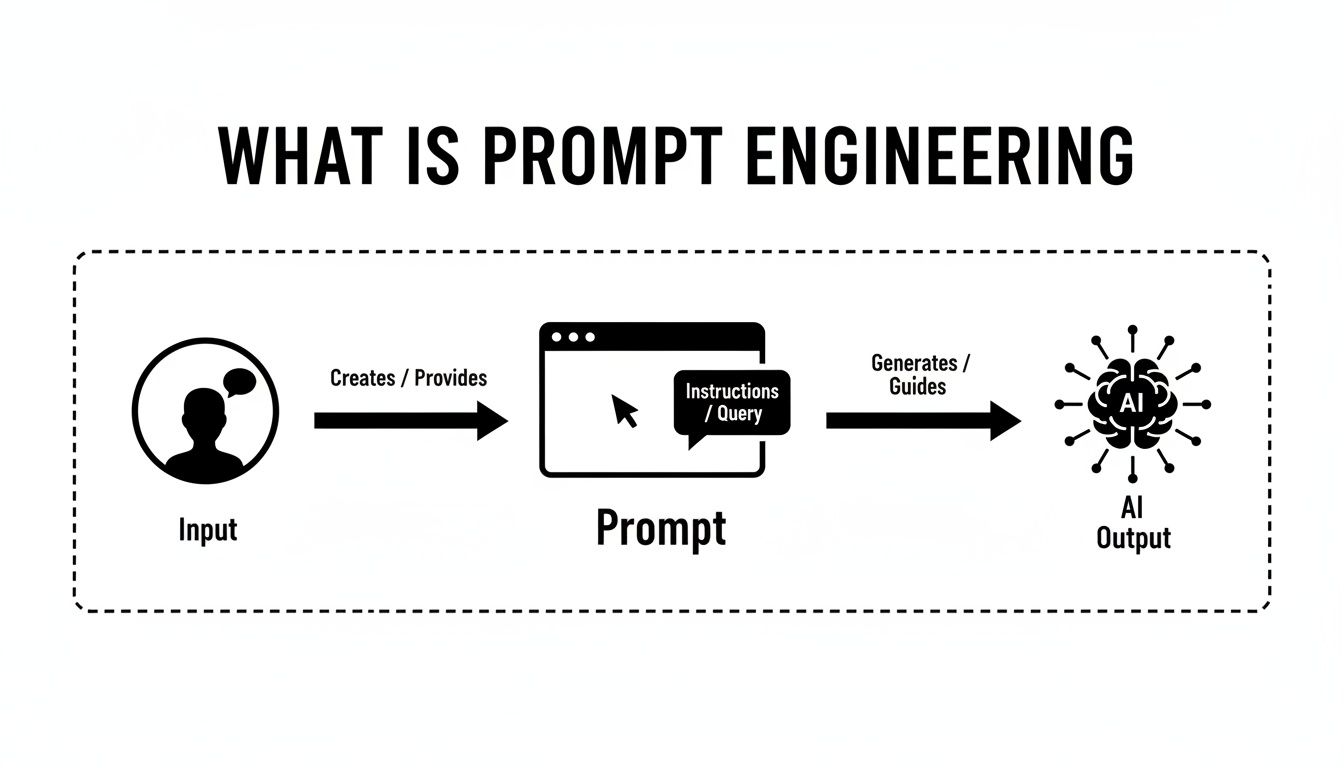
As you can see, the prompt itself is the critical bridge connecting your intention to the AI's final action.
Provide Absolute Clarity And Specificity
The single biggest mistake people make with prompts is being vague. An AI can't read between the lines or guess your intent; your instructions have to be direct and impossible to misinterpret. Ambiguity gets you ambiguous, often useless, results.
It’s like giving someone directions. "Head downtown" is basically useless. But "Drive south on Main Street for three blocks, then turn left on Oak Avenue" is a clear, actionable path. The same logic applies to prompts.
- Weak Prompt: "Explain our return policy."
- Strong Prompt: "Explain our 30-day return policy for unopened products. Mention that the customer needs the original receipt and is responsible for shipping costs."
That level of detail removes all the guesswork. It forces the AI to focus only on the essential information, giving you a much more accurate and complete answer right away.
Give The AI Sufficient Context
Context is all the background information the AI needs to understand the why behind your request. Without it, the model is flying blind. Providing context is like giving a baker the full recipe instead of just handing them a bag of flour—it makes sure the final product actually makes sense.
For instance, if you ask an AI to write an email, it needs to know who you're writing to, what the goal is, and any relevant history. This background dramatically changes the tone, content, and structure of its response.
Providing rich context is the single most effective way to improve the relevance and quality of an AI's output. It anchors the model's vast knowledge to your specific situation.
This idea has been a game-changer in AI. A huge milestone came in January 2022 when researchers introduced Chain-of-Thought prompting, a technique that teaches models to reason through problems step-by-step. By September 2023, we saw frameworks like DSPy emerge, which can automatically add context and examples to prompts, proving just how vital this element is. You can learn more about the history and evolution of prompt engineering to see how these ideas came to be.
Set Clear Constraints And Rules
Constraints are the guardrails you put on the AI's output. By setting specific rules, you dictate exactly how you want the information presented, ensuring it's structured for your exact needs. This is where you really take control of the final result.
Common constraints you can apply include:
- Word Count: "Summarize this in under 50 words."
- Output Format: "Provide the answer as a JSON object." or "List the key points in a bulleted list."
- Negative Constraints: "Do not mention our competitors." or "Avoid using technical jargon."
Applying constraints stops the AI from rambling or giving you information in a format you can't use, saving you a ton of time on editing.
Assign A Persona For Tone And Style
Finally, assigning a persona tells the AI how to say something. This is a powerful shortcut that instantly shapes the model's voice, tone, and personality without you having to describe it in painstaking detail.
- "Act as a friendly and empathetic customer support agent."
- "You are a formal business analyst creating a report."
- "Adopt the persona of a patient and encouraging technical instructor."
When you define a role, you tap into the model's vast training data associated with that persona. This ensures the response aligns perfectly with your brand's voice and the specific needs of the conversation.
Essential Prompting Techniques You Can Use Today
The principles behind good prompting give you the "why," but the techniques are all about the "how." This is where theory meets practice, and you really start to see what prompt engineering can do. We're going to walk through some powerful, hands-on methods you can start using right now to get better results from any large language model.
We'll begin with the foundational strategies, which show how just a few simple examples can drastically improve an AI's accuracy. From there, we'll get into more advanced methods designed to unlock complex reasoning and problem-solving.

To make this super practical, every technique will be demonstrated with clear examples tailored for customer support, so you can immediately see the real-world impact.
Foundational Shot-Based Prompting
One of the most intuitive ways to guide an AI is to simply show it what you want. This family of techniques is called "shot-based" prompting, where each example you provide is a "shot." The number of shots you give the model determines the specific technique.
1. Zero-Shot Prompting
This is prompting in its purest form. You give the AI a direct command without providing any examples to follow. It's a straight shot, relying entirely on the model's vast pre-existing knowledge to figure out your intent.
- When to use it: Perfect for simple, common tasks where the AI is highly unlikely to get confused.
- Example for an AI Support Agent: "Summarize the following customer complaint: 'I ordered a blue widget, but I received a red one. My order number is 12345, and I'm very frustrated because I needed it for an event this weekend.'"
Summarization is a core skill for these models, so it can handle this request easily without any hand-holding.
2. One-Shot Prompting
With this technique, you provide a single, high-quality example of the output you're looking for. Think of it as giving the AI a perfect template to copy. This single example can dramatically improve accuracy, especially when you need a specific format or style.
- When to use it: When you need the output to follow a specific structure that the AI might not generate on its own.
- Example: "Extract the key information from customer emails. Format it as:
Product: [product name],Issue: [brief description].- Example Input: 'My Pro-Series blender is making a weird rattling noise.'
- Example Output:
Product: Pro-Series blender,Issue: Rattling noise - New Input: 'The left earbud of my SonicWave headphones won't charge.'"
That one perfect example is all it takes to guide the AI to produce a consistently formatted answer for the new input.
3. Few-Shot Prompting
As the name suggests, you provide a few examples—typically 2-5. This method is incredibly effective for teaching the AI to handle more nuanced or complex tasks. By showing it how to navigate different variations of a problem, you build its understanding of the underlying pattern.
- When to use it: For tasks that involve pattern recognition, subtle classification, or dealing with a variety of user inputs.
- Example: "Categorize these support tickets as either 'Billing,' 'Technical,' or 'Shipping.'
- Ticket 1: 'My credit card was charged twice.' -> Billing
- Ticket 2: 'I can't log in to my account.' -> Technical
- Ticket 3: 'Where is my package?' -> Shipping
- New Ticket: 'My invoice for last month is incorrect.'"
Seeing multiple examples helps the model grasp the logic behind the classification, making it far more reliable.
To help you decide which shot-based method to use, here’s a quick breakdown of how they compare.
Comparing Prompting Techniques
This table gives a side-by-side look at the primary prompting techniques, helping you pick the right one for the job.
| Technique | Description | Best For | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Shot | Giving a direct instruction with no examples. | Simple, straightforward tasks like summarization or general questions. | "What is the capital of France?" |
| One-Shot | Providing a single, high-quality example to follow. | Tasks requiring a specific format, style, or tone. | "Translate 'hello' to French. Example: 'goodbye' -> 'au revoir'." |
| Few-Shot | Offering 2-5 examples to teach a pattern or logic. | Complex classification, sentiment analysis, and nuanced tasks. | Providing several examples of positive and negative reviews to classify a new one. |
Choosing the right technique is often about balancing simplicity with the complexity of your task. Start with zero-shot and add examples only when you need more control or accuracy.
Unlocking Advanced AI Reasoning
While showing examples is great for formatting and classification, some problems require the AI to actually think through multiple steps. That’s where more advanced techniques come into play.
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting
Chain-of-Thought is a deceptively simple yet powerful technique. Instead of just asking for the final answer, you instruct the AI to "think step-by-step." That’s it.
This small change encourages the model to break down a complex problem into a sequence of smaller, logical steps, write them out, and then arrive at a conclusion. It’s a game-changer for reducing errors in math, common sense puzzles, and symbolic reasoning tasks.
By forcing the AI to show its work, Chain-of-Thought prompting mimics human problem-solving and dramatically improves the reliability of its conclusions for complex queries.
Let's see how this works in a support scenario.
- Before CoT: "A customer's subscription costs $30/month. They were incorrectly billed for three months. How much should they be refunded?" -> The AI might just spit out $90.
- After CoT: "A customer's subscription is $30/month. They were incorrectly billed for three months. Let's think step-by-step to calculate the correct refund."
The AI's response would then look something like this:
- The monthly cost of the subscription is $30.
- The customer was incorrectly billed for 3 months.
- To find the total refund, I need to multiply the monthly cost by the number of months.
- $30 * 3 = $90.
- The total refund should be $90.
This step-by-step process makes the AI's reasoning transparent and far more likely to be correct.
The field is constantly evolving with new methods built on these core ideas. In 2023, an approach called prompt tuning emerged, which allows for fine-tuning with minimal data and has been shown to outperform older benchmarks by 15% in some studies. Similarly, techniques like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) have boosted model performance by as much as a 30% improvement.
If you're interested in the history and evolution of these methods, you can explore some of the key milestones in prompt engineering. Combining these foundational techniques with more advanced strategies gives you a robust toolkit for guiding AI behavior effectively.
Prompt Engineering in Action for AI Support Agents
Theory is great, but let's be honest—the real "aha!" moment comes when you see prompt engineering solve a real-world problem. For customer support teams, the gap between a fuzzy prompt and a well-crafted one is massive. It can be the difference between a happy customer and an angry escalation.
So, let's get practical. We’ll walk through a few common support scenarios, dissecting a "bad" prompt and a "good" one for each. This side-by-side look will show you just how a few tweaks—adding clarity, context, constraints, and a persona—can turn a generic AI into a world-class support agent.

Scenario 1: De-escalating a Frustrated Customer
Dealing with an upset customer is tricky. You need a careful mix of empathy, speed, and clear answers. The AI has to validate their feelings without making empty promises, all while guiding them to a solution. In these high-stakes moments, the tone is everything.
Bad Prompt:
"Customer is angry about their bill. Explain why it's correct."
This prompt is basically asking the AI to start a fight. It’s confrontational, offers zero context about why the customer is upset, and completely ignores the need for an empathetic tone. You’re practically guaranteed a terrible response.
Good Prompt:
Persona: Act as a patient and empathetic support specialist named Alex. Context: A long-time customer is frustrated because their monthly bill increased from $50 to $70 unexpectedly. They believe it's a billing error. The reason for the increase is that their 12-month promotional discount has expired. Task: Draft a response that:
- Acknowledges their frustration and validates their concern.
- Gently explains the promotional period has ended, referencing the original terms.
- Avoids blaming the customer ("you didn't read the terms").
- Offers to check their account for any new available discounts or promotions.
- Maintains a helpful and apologetic tone throughout.
See the difference? This prompt is worlds better. It gives the AI a name and personality, provides the backstory, and breaks the task into five clear steps. The specific instructions on what not to do are just as important, ensuring the AI de-escalates the situation instead of making it worse.
Scenario 2: Guiding a Non-Technical User
It’s a classic challenge: walking a new user who isn't tech-savvy through a setup process. The goal here is to be simple, encouraging, and avoid jargon at all costs. You want to build their confidence, not overwhelm them.
Bad Prompt:
"Tell the user how to set up their account."
This is way too broad. What does "set up" even mean? Which part are they stuck on? The AI has to guess, which usually results in a generic, unhelpful list of steps that misses the user's actual problem.
Good Prompt:
Persona: You are a friendly and encouraging onboarding guide. Context: A new user has just signed up for our "PhotoCloud" service but is stuck. They don't know how to upload their first photo from their computer. Task: Write a simple, numbered list of no more than 4 steps to guide them. Use non-technical language (e.g., use "click the button with the cloud icon" instead of "initiate the upload function"). Start by congratulating them on creating their account.
This is perfect. The persona sets a welcoming tone, the context pinpoints the exact problem, and the task gives clear, structured instructions. The constraints—like "no more than 4 steps" and "use non-technical language"—are the guardrails that keep the AI's response focused and easy to follow.
Key Takeaway: The more specific your instructions, the less the AI has to guess. A detailed prompt acts as a comprehensive brief, leading to a tailored and effective output every time.
Scenario 3: Summarizing a Problem for Escalation
When a ticket needs to be passed to a higher tier, the handoff has to be seamless. A great summary lets a senior tech grasp the issue instantly, without having to dig through a long chat history.
Bad Prompt:
"Summarize this chat log for the technical team."
This prompt will probably get you a summary, but it won't be the one your engineers need. It will likely be a long, narrative recap instead of the structured, scannable brief that actually saves time.
Good Prompt:
Persona: You are a detail-oriented Tier 1 support agent. Task: Summarize the following customer conversation for escalation to the Tier 2 engineering team. Format the output using the following template:
- User: [Customer Name and User ID]
- Issue: [A one-sentence summary of the problem]
- Troubleshooting Steps Taken: [A bulleted list of all steps the agent and user have already tried]
- System Details: [Extract the user's operating system and browser version from the chat]
- Next Steps: [Recommend a specific action for the Tier 2 team] Chat Log: [Paste the full conversation here]
This prompt is a masterclass in getting exactly what you need. It uses a template to force the output into a specific, highly useful format. Every critical piece of information has its place. This structured approach cuts down on back-and-forth and gets problems solved faster.
This is where building predefined prompts into your workflow becomes so powerful. Tools like SupportGPT let you create these kinds of structured AI interactions, making your support process not just faster, but smarter and more consistent.
Of course. Here is the rewritten section with a more natural, human-expert tone.
Common Prompting Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Knowing the right techniques is a great start, but spotting what not to do is just as critical. Even seasoned pros fall into common traps that lead to confusing, inaccurate, or just plain unhelpful AI responses. Think of these mistakes less as failures and more as learning opportunities that sharpen your instincts.
Once you can recognize these pitfalls, you'll be able to troubleshoot your own work and build more reliable AI interactions from the ground up. Let's walk through some of the most frequent blunders and how you can steer clear of them.
The Pitfall of Vague Instructions
This is, by far, the most common mistake. Being too ambiguous or vague with your request is a recipe for disaster. An AI can't read your mind or guess what you really mean, so fuzzy prompts get you fuzzy results. For precise outputs, you have to be crystal clear.
- Bad Prompt: "Write about our new feature."
- Good Prompt: "Write a three-paragraph announcement for our blog about the new 'Project Dashboard' feature. Explain how it helps users track task progress in real-time. Use a friendly and excited tone."
See the difference? The second version gives the AI a clear task, topic, format, key benefit, and even a personality. It removes all the guesswork. A good rule of thumb is to always assume the AI knows nothing about your goals unless you spell it out.
The Problem with Conflicting Rules
It’s surprisingly easy to give an AI contradictory instructions, especially in a longer prompt. When the model gets mixed signals, it gets confused and the output quality tanks. A classic example is asking for a "brief, comprehensive report"—which is it? Brief or comprehensive? The AI has to pick one, and it might not be the one you wanted.
Key Insight: Treat your prompt like a legal contract. Every word matters, and any ambiguity or contradiction can be misinterpreted. Always give your instructions a quick once-over to make sure they're consistent before you hit send.
A great way to avoid this is to break down complex requests into smaller, sequential steps. Make sure each new instruction builds on the last one without creating a conflict. This kind of clarity is a cornerstone of effective prompt engineering.
Forgetting to Set a Clear Persona
Skipping the persona is a massive missed opportunity to control the AI's tone and style. If you don't give the model a role to play, it will default to its standard voice: neutral, generic, and often a bit robotic. That's probably not what you're looking for, especially if it needs to match your brand or a specific situation.
- Without Persona: "Explain why the customer's payment was declined."
- With Persona: "Act as an empathetic and patient support agent. Gently explain to the customer that their payment was declined due to an expired card, and guide them on how to update it."
Assigning a persona is a powerful shortcut. It's one of the fastest ways to shape the entire feel of the response.
Failing to Test and Refine Your Prompts
Finally, a huge mistake is writing a prompt, getting a so-so result, and just giving up. Great prompting is rarely a one-shot deal; it's an iterative process. Your first try is almost never your best one.
Real success comes from a simple feedback loop: you test, you analyze the output, and you tweak your instructions based on what you learned. Treat every interaction like a mini-experiment.
- Test: Run the prompt and see what comes back.
- Analyze: Figure out exactly where the AI went off the rails. Was it the tone? The format? Did it hallucinate a fact?
- Refine: Adjust your prompt to fix that specific issue. Maybe you need to add more context, set a clearer boundary, or provide a better example.
This cycle of continuous refinement is what separates the novices from the experts. If you embrace this process, you'll be able to methodically improve your prompts until they deliver exactly what you need, every single time.
Your Next Steps in Mastering Prompt Engineering
Think of this guide as your starting point, not the finish line. Reading about prompt engineering is one thing, but true mastery is forged in the trenches—through constant practice, experimentation, and a willingness to learn from what works and what doesn't. You now have the foundational principles, but the real skill comes from getting your hands dirty.
The most important part of this whole process? Iteration. Nobody writes the perfect prompt on their first try. It's more like sculpting. You start with a rough idea, test it, look at what the AI gives you back, and then you tweak your instructions. This cycle of testing and refining is how you go from theory to tangible results.
Embrace the Prompt Playground
To get good at this, you need a safe place to fail. That’s where a prompt playground comes in. Think of it as a sandbox environment where you can test-drive your prompts without messing up live customer conversations or your team's workflow. It's your personal lab for experimentation.
A prompt playground is your space to get creative, see what the AI is capable of, and polish your instructions until they're perfect—all without any real-world consequences.
In a playground, you can see firsthand how a tiny change in phrasing or adding a single piece of context can completely change the AI's output. It's the best way to build an intuitive feel for how these models think and respond.
Your First Practical Challenge
Alright, time to move from reading to doing. The quickest way to make these concepts stick is to put them to work right now. This is your chance to turn what you’ve learned into a valuable, practical skill.
Here’s your first challenge:
- Pick a common customer question. Grab a query your team gets all the time—something about a product feature, a billing question, whatever.
- Draft an advanced prompt to answer it. Use the core ideas from this guide: be clear, provide context, define a persona, and set constraints.
- Incorporate a specific technique. Try structuring your prompt using Chain-of-Thought to guide its logic or Few-Shot prompting to show it exactly what a good answer looks like.
- Test and refine it. Take your prompt to a playground and keep tweaking it until the AI’s response is consistently spot-on.
This one exercise will do more for your learning than hours of reading. It’s the first step toward becoming a genuinely skilled prompt engineer.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers.
As you start exploring what AI can do, you'll naturally have a few questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones about prompt engineering to clear things up.
Do I Need to Know How to Code to Do This?
Not at all. This is one of the biggest misconceptions out there. While a technical background doesn't hurt, especially for complex projects, the heart of prompt engineering is about communication, not code. It’s a skill rooted in logic, clarity, and a bit of creativity.
You're essentially becoming a great communicator with an AI. Tools like SupportGPT are built for exactly this, empowering non-technical users to create sophisticated AI agents with plain English.
How Is This Different From "Training" an AI?
This is a crucial distinction. Training an AI model, often called fine-tuning, is a heavy-duty process. It involves feeding the model enormous amounts of data to fundamentally change its internal workings. It's expensive, time-consuming, and requires a team of specialists.
Prompt engineering, on the other hand, works with an AI that's already trained. You aren't altering the model's core. You're just getting really, really good at giving it instructions to steer its vast knowledge toward the exact result you want.
Think of it as the difference between teaching someone a new language from scratch versus giving a fluent speaker clear directions. It’s a much faster and more accessible way to customize AI behavior.
Will AI Get So Smart That We Won't Need Prompt Engineering Anymore?
It's a fair question, but prompt engineering isn't going anywhere. Sure, AI models are getting better at figuring out what we mean even when our instructions are a bit fuzzy. But for business-critical tasks, "close enough" doesn't cut it.
The need for precision, safety, and reliability only grows as we give AI more important jobs. The ability to craft instructions that are clear, context-aware, and aligned with specific goals will become more valuable, not less. The methods might change, but the fundamental skill of expertly guiding AI will remain essential.
Ready to build an AI agent that actually gets it right every time? With SupportGPT, you can launch a smart assistant trained on your own knowledge base in minutes. Start your free trial today and see what precise prompting can do for you.